Hidradenitis Suppurativa
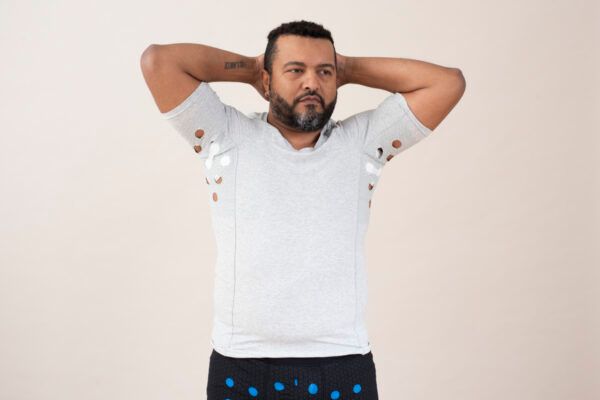
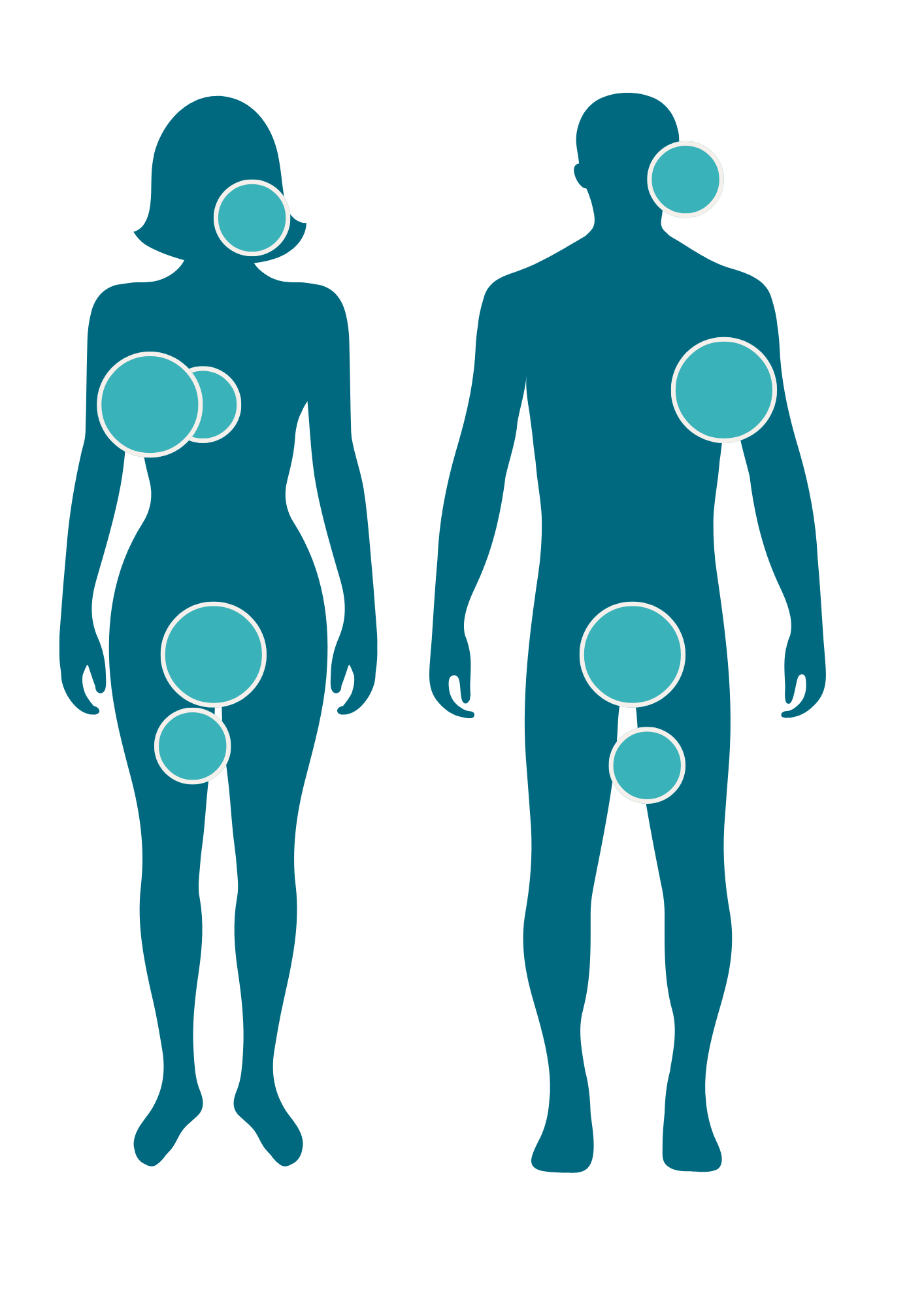
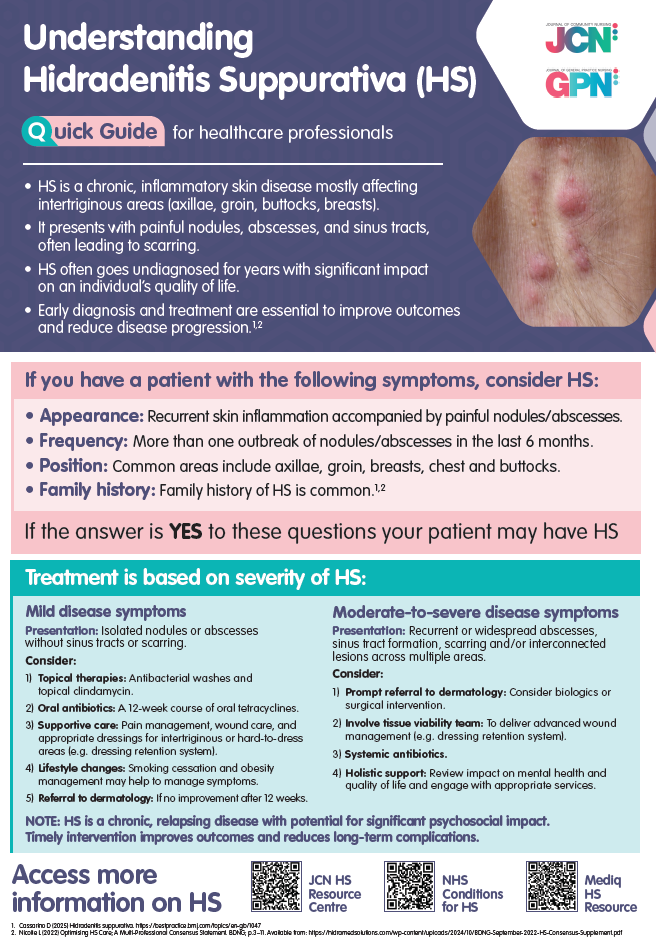
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes recurring boils in the folds of your skin and is characterised by painful nodules, abscesses, sinus tract formation, and scarring.
Diagnosing Hidradenitis Suppurativa
Diagnosis is clinical and often delayed due to misidentification, particularly in early stages.
A diagnosis of HS can typically be made when the following are present:
A diagnosis of HS can typically be made when the following are present:
Assessment and Clinical History
When assessing for HS, clinicians should take into account:
When assessing for HS, clinicians should take into account:
Physical Examination
Examination should include:
Examination should include:
1. Nodules and abscesses
2. Sinus tracts and scarring
3. Discharge, malodour, or signs of secondary infection
2. Sinus tracts and scarring
3. Discharge, malodour, or signs of secondary infection
Investigations
While HS is a clinical diagnosis, the following may support management:
While HS is a clinical diagnosis, the following may support management:
Common Pitfalls in Diagnosis
Mangement
Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is a chronic skin condition that develops in stages. Recognising the three stages of HS (Hurley Stages I–III) can help patients and healthcare professionals make informed decisions about treatment and care.
Stage 1 – Mild (Early Stage)
Early signs can often be mistaken for boils or ingrown hairs. Seeking advice early can make a big difference.
Stage 2 – Moderate
This stage can significantly affect comfort and mobility. Managing HS at this point often involves a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle changes.
Stage 3 – Severe
Severe HS can be debilitating. Specialist care is usually needed, and surgery may be recommended to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment
In the UK, treatment for Hidradenitis Suppurativa (HS) is typically led by a dermatologist. Treatment is tailored to the severity and stage of the condition and focuses on reducing inflammation, managing symptoms, and preventing progression.
GP referral to dermatology is essential for moderate to severe HS
Here’s an overview of treatment options available to the patient:
Lifestyle and Self-Care
Medical Treatments
Surgical Options
Adjunctive Therapies
Education
Our Mission
We deliver the right and the most efficient outcomes to European Healthcare by providing products, services, and solutions.